China is sitting on a cash pile of US$3.8 trillion and recent data suggests that its outbound direct investments (ODI) have risen to almost the same level as in-bound foreign direct investment (FDI). If the trend continues, China will soon be a net outbound investor.
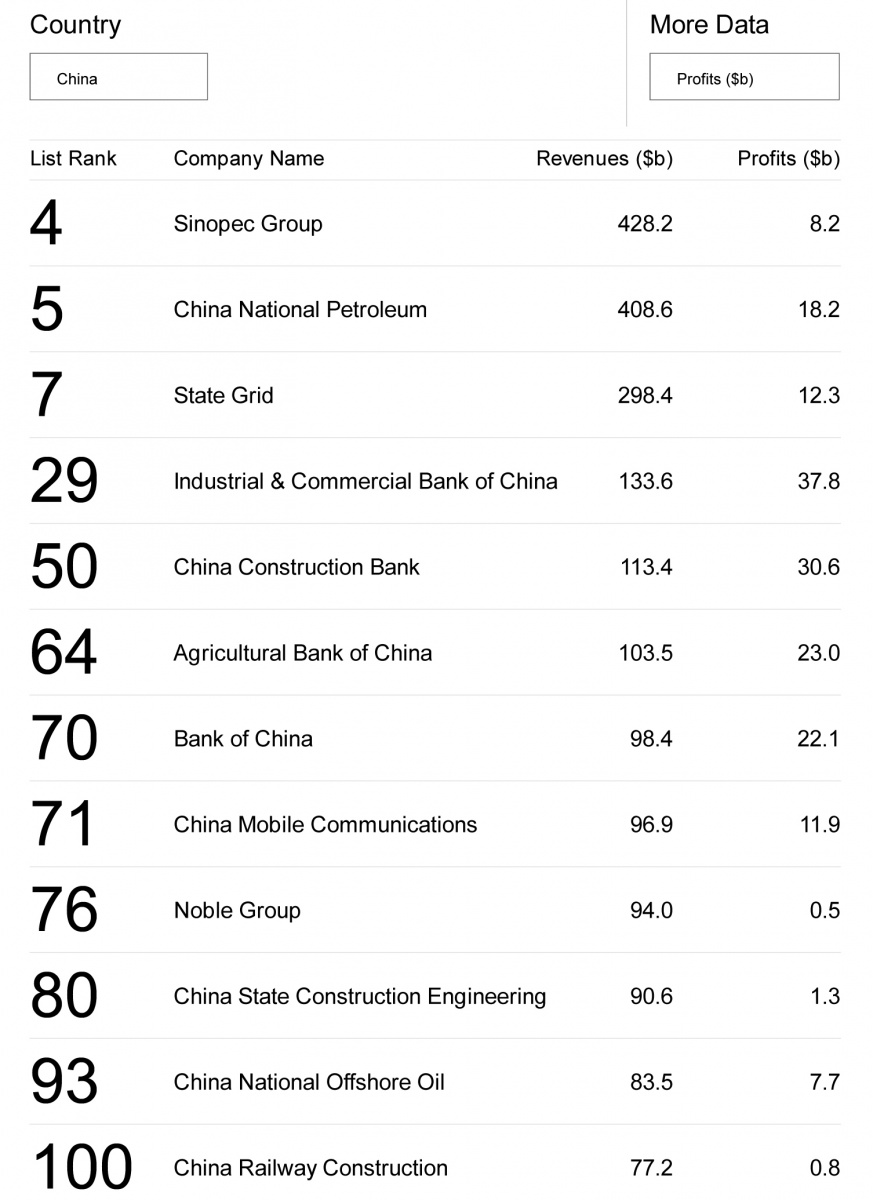
One key area for investment could and perhaps should be in acquiring international brands that would enable, particularly the Chinese national champions and the other large players (there are 89 Chinese companies in the latest Fortune Global 500 list), to leap on to the world stage rapidly and without the baggage of the Chinese country-of-origin (see last week’s blog).
The challenge, should we see a spate of such acquisitions, will be integration. The history of Chinese international acquisitions is mixed, much more so than that of companies from its other large Asian neighbor, India. Thus, for instance, TCL acquired Thompson of France back in the early days of this century, an acquisition that almost took it under.
Why did the acquisition fail? On the one hand, TCL’s bet on the rear-projection TV technology, a technology in which Thompson was a leader, did not pan out, as plasma and LCD screens came to dominate that industry. But, equally, TCL struggled with the integration of Thompson in to its business. Cultural differences in many ways proved insurmountable.
So what can Chinese acquirers learn from the much more successful acquisitions undertaken by Indian firms? The most important lesson is, humility is essential. While Chinese firms are arrogant and believe like many Western acquirers, that there is little to learn from the acquired company and that they can improve the performance of the acquired company by implementing their own and superior systems and processes, injecting their superior and more hardworking executives to “run the show”, and doing so at the much faster “China speed” that they are used to, Indian firms acquire with the view to learn what is good from the acquired company, improve what is not so good by injecting their own capabilities, and doing so gradually. In some sense, the old adage of being slow and steady to win the race applies equally to acquisitions.
To take this more humble but successful approach, perhaps the most difficult step will be to learn humility. Swept away by the “China Dream”–an idea that has been around for a while, but now is reaching fever pitch, pushed by the efforts of the current administration under President Xi Jinping–there is a general view of Chinese superiority which blinds acquirers to the superior aspects of the acquired firm, which, ironically, was the reason for the acquisition in the first place!
With humility in place, the rest is relatively easy. You can read more about that in my “The New Emerging Market Multinationals: Four Strategies for Disrupting Markets and Building Brands”. Indeed, a bit of humility and with the right acquisition team and process, Chinese companies could start becoming the acquirers of choice, just as the Indian acquirers have successfully become.



